A battery can be regarded as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance, which is called internal resistance. When the battery works, the voltage output is lower than the open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV). The difference is the voltage drop caused by the internal resistance. Internal resistance represents the battery’s limiting factor to deliver the required current and/or supply the required energy. High internal resistance results in high voltage drop on the loaded battery and increased heat generation in the battery under load, i.e unwanted energy loss. In many devices high battery internal resistance will speed up reaching the battery cut-off voltage and triggering an early shutdown of the battery powered device.
The internal resistance is measured by ohm (Ω). The value of internal resistance varies depending on multiple factors, such as battery size, cathode electrode, anode electrode, separator, electrolyte, temperature, and state of charge (SOC) of the battery. Internal resistance is one of the parameters that indicate a battery’s ability to carry current.
When the value of internal resistance is low, the battery is able to carry a significant amount of current. On the other hand, a battery with high internal resistance can only carry a small amount of current. One reason for measuring internal resistance is for battery maintenance: The internal resistance of a battery gradually increases as it is used. By measuring the internal resistance of the battery on a regular basis, a degraded battery can be eliminated before it becomes a problem.
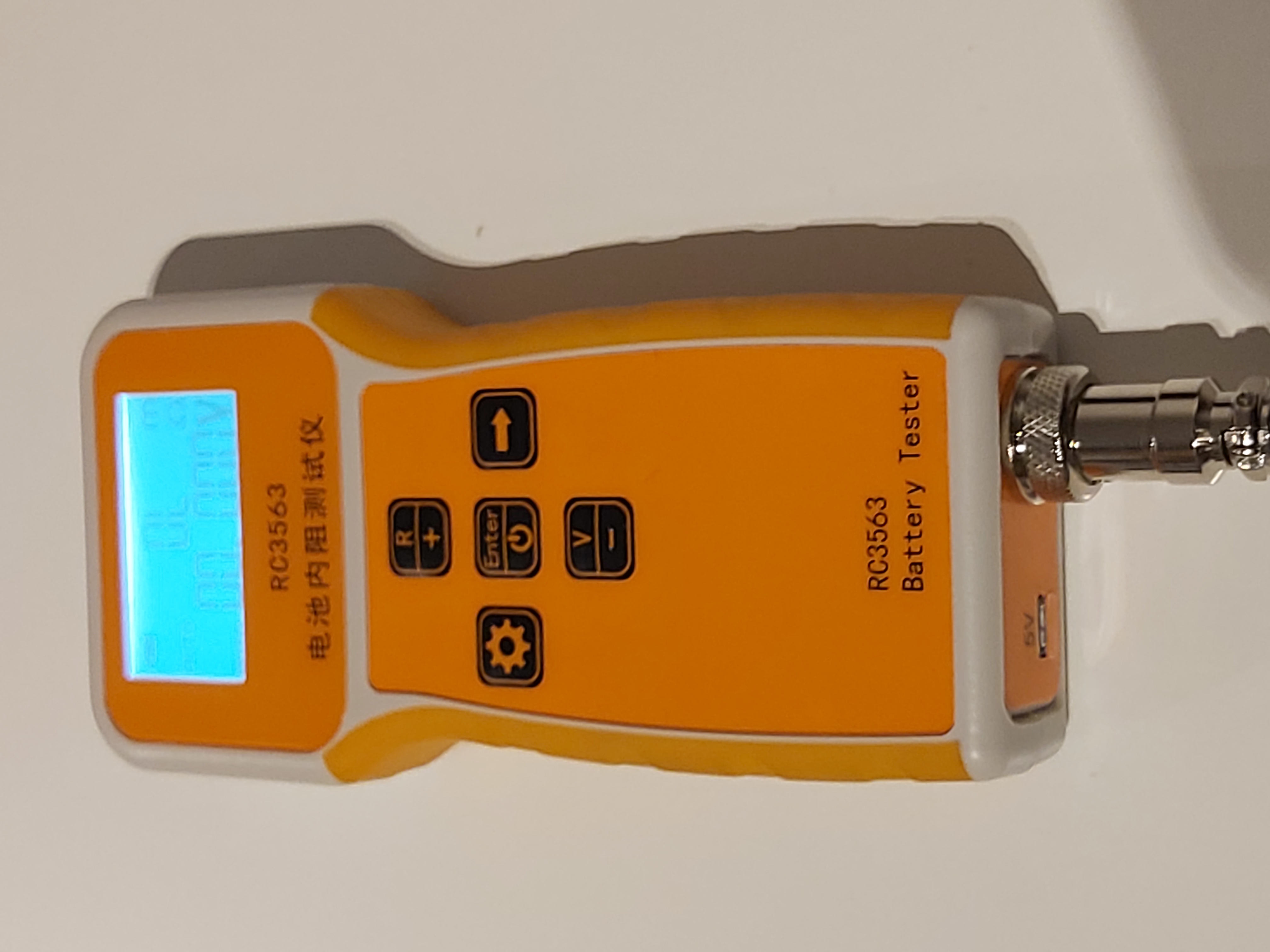
To measure the battery internal resistance, a special instrument designed for this is the the best option to use. I ordered some time ago RC3563 Lithium Battery Internal Resistance Tester with 4-wire Probes to be able to measure battery internal resistance (and other low resistances).
The RC3563 battery internal resistance tester can measure internal resistance and voltage of the battery at the same time. It is very nice to get the measurement results of both resistance and voltage at the same time. RC3563 can accurately test internal resistance of your batteries with voltage range of 0-100v. RC3563 can also measure low resistance resistor values.
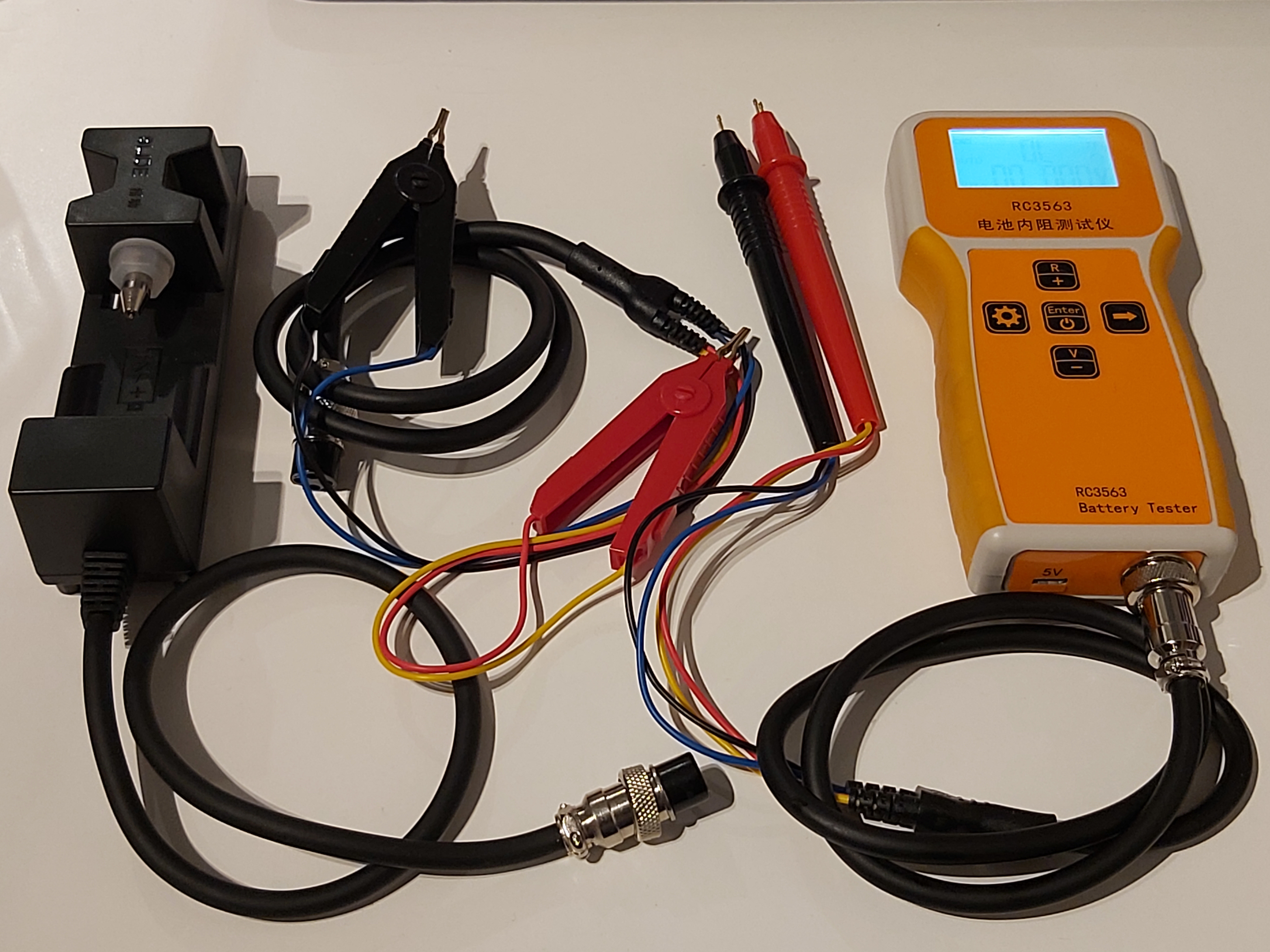
The measurement with RC3563 battery internal resistance tester is done using the Kelvin four-wire test clamp. Kelvin four-wire method avoids the influence of contact resistance and wire resistance (when used correctly), so accurate measurement can be performed.
Specifications:
Speed: 5 times/second
Adjustment: Correction for resistance and voltage separately
Basic accuracy:
Resistance: 0.5%
Voltage: 0.5%
Measuring ranges:
Resistance: 0.0001mΩ~200Ω
Voltage: 0.0001V~±100V direct current
Resistance ranges: 6 ranges automatic and manual
Voltage ranges: 3 ranges automatic and manual
Battery: 1 * lithium battery, 1000mAh (included)
Package size: 180 * 90 * 35mm / 7.1 * 3.5 * 1.4in
Package weight: 250g / 8.8ounce
This tester adopts intelligent control and large display, also with built-in 1000mAh lithium battery.
According to manufacturers the instrument can measure any type of batteries, including lithium batteries, lead-acid batteries, nickel-chromium batteries, dry batteries and so on. You can measure batteries of any capacity, no matter how big it is, as long as the internal resistance is within 0-200 milliohms and the voltage is within 100V. The battery’s full and depleted state will not affect the battery’s internal resistance, and can be measured, with minimal changes in internal resistance (except for defective batteries).
When I ordered the meter, I ordered few different test clamps suitable for different uses.
The RC3563 battery internal resistance tester uses AC resistance measurement method. So the tester gives Alternating Current Internal Resistance, commonly called AC Impedance or Impedance
. This tester seems to give quite accurate reading of battery internal resistance. The measurement works correctly even without battery voltage present, so RC3563 can also be used to measure the AC resistance of low-ohms resistors. Because the AC measurement method (around 1 kHz signal), this meter cannot be used to measure RC resistance of inductive components like coils, transformers or electric motors.
From: https://github.com/ludwich66/RC3563/wiki
Measurement AC Resistance DC Voltage
Accuracy Resistance 0,5% Voltage 0,5%
Range 1 µΩ – 200 Ω 1 mV – 100 V DC
Ranges 6 3
Current 2 mΩ @ 50mA
Current 20 mΩ @ 50mA
Current 200 mΩ @ 5mA
Current 2 Ω @ 5mA
Current 20 Ω @ 0,5 mA
Current 200 Ω @ 0,5 mA
Test signal frequency: AC 1 kHz
Here are some videos of RC3563:
Battery tester RC3563
High Precision Li Ion Battery Internal Resistance Tester RC3563 Close view
RC3563 battery tester – Excel and automatic measurements / PC communication (18650) video presents a way to connect the RC3563 meter to a computer and semi-automatic data reading using an excel sheet.
When I received the meter, I had some problems with the measurements. The situation was somewhat similar to RC3563 Battery Tester (inconsistent readings?) video that shows inconsistent Internal Resistance readings from meter. I originally had a similar problems that the internal resistance and voltage results were inconsistent.
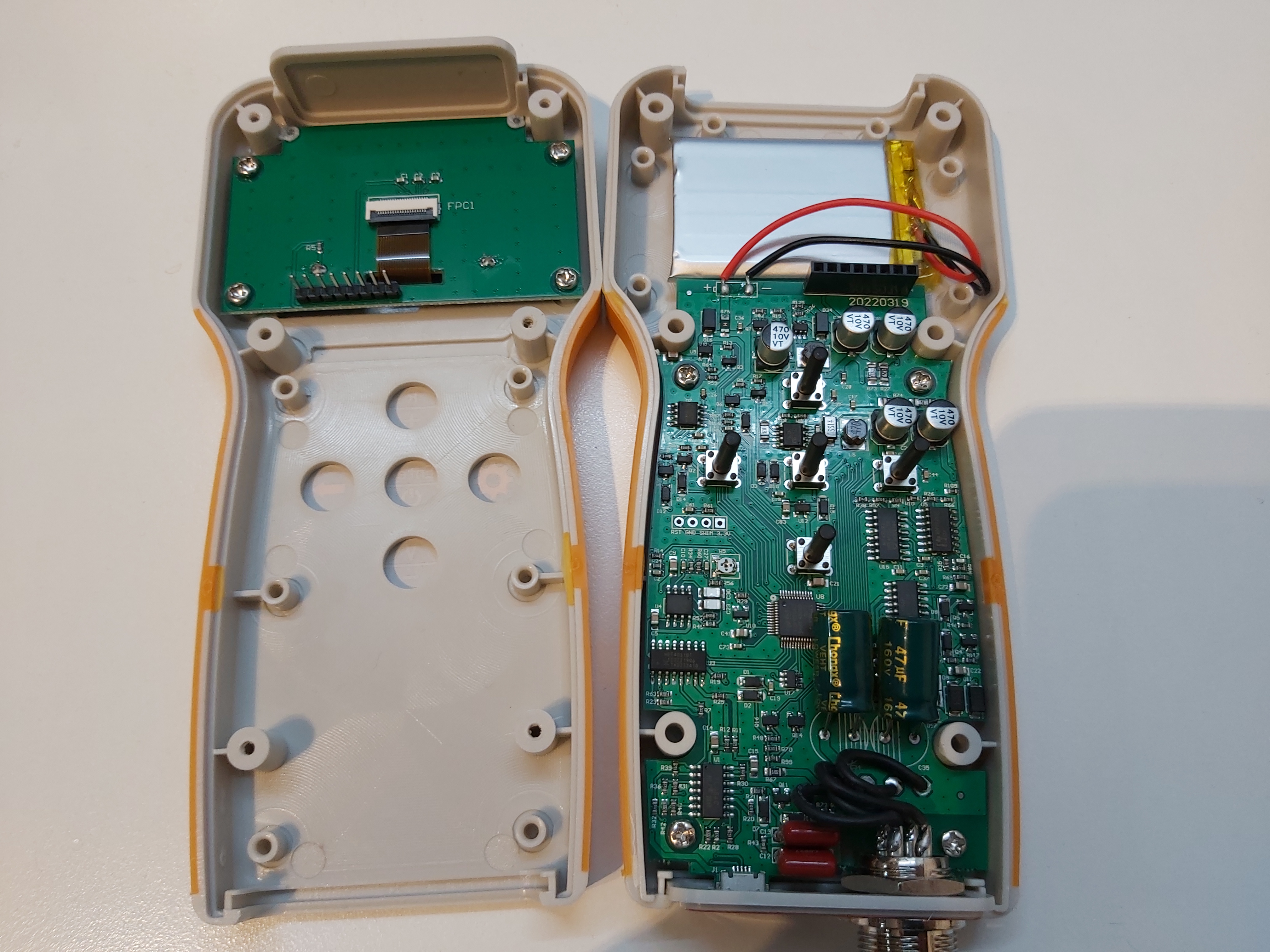
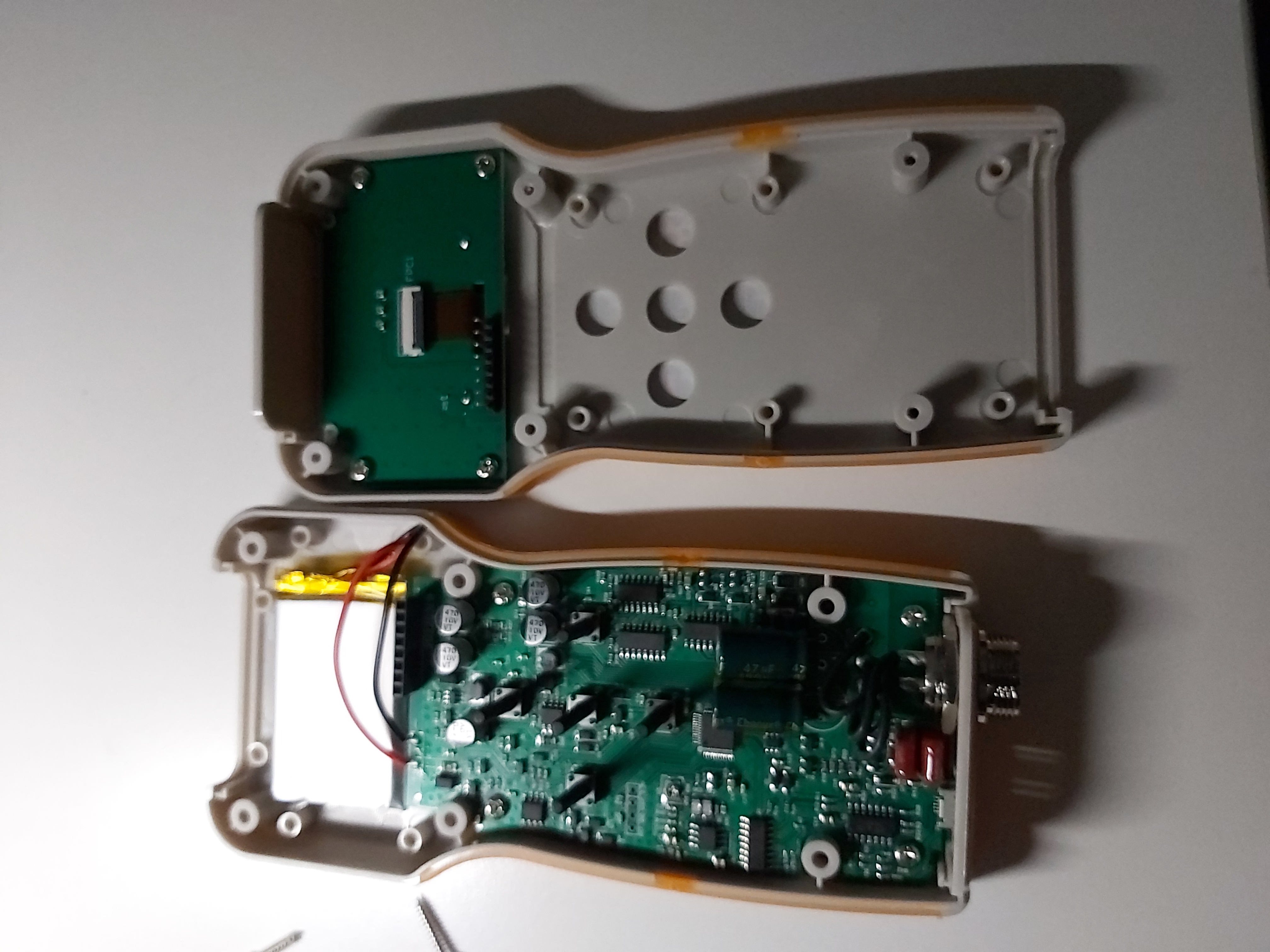
I opened the meter and did some investigation.
After some investigation I found out that there were some bad soldering joints inside the meter with the two big electrolytic capacitors in the measurement circuit. After re-soldering the problem was solved.
If the meter itself is OK, but test result are unstable, it may be that the test clip is in poor contact with the battery, or the battery under test is unstable, the electrode has an oxide layer, or there is a strong magnetic field around it.
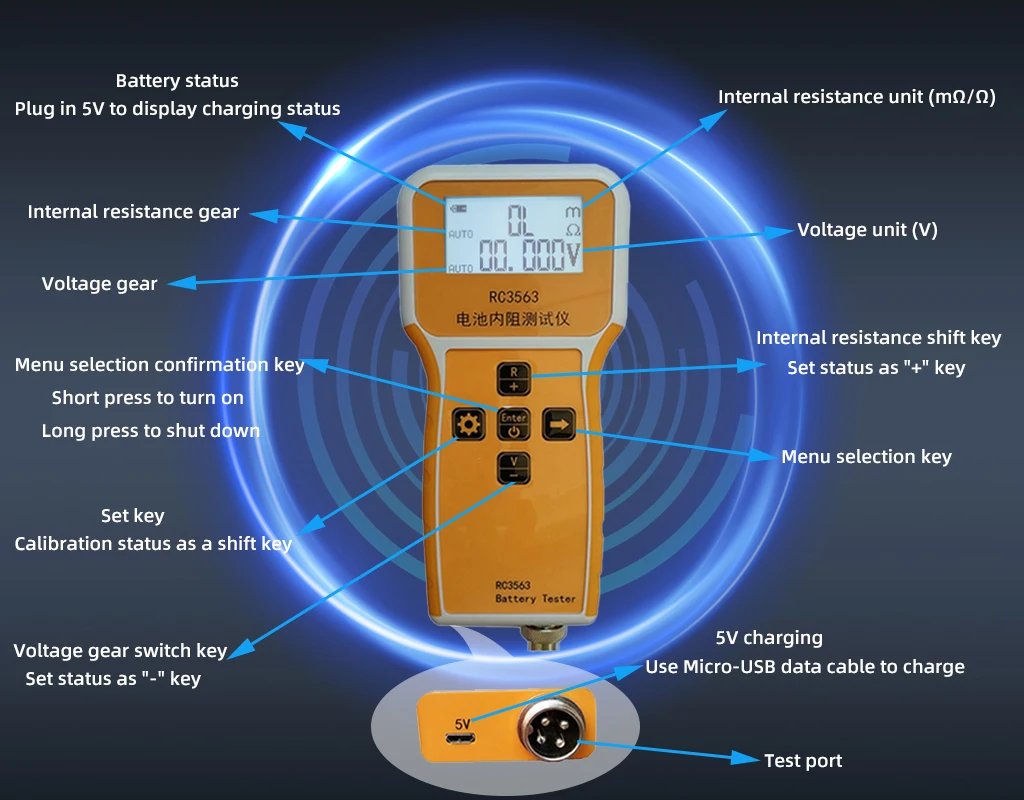
Instructions for use:
1. Short press “enter key ” to turn on.
2. Long press “enter key ” to shut down.
3. Press the “set key” to enter the setting state, then press the “select key” to select different functions, and then press the “enter key” to enter the corresponding function.
4. Enter the resistance calibration/voltage calibration state. At this time, the test line should clamp the calibration resistance or voltage, press the “set key” to select the gear to be calibrated, and then press “+” and “-” to adjust the displayed value to be equal to the calibration resistance or voltage , Press the “select key” to select “ok” or “Cancel”, and finally press the “enter key ” to decide whether to save or cancel.
Documentation links:
https://github.com/ludwich66/RC3563/blob/main/RC3563_Manual_English.pdf
https://www.scribd.com/document/660147456/RC3563-Manual-English
RC3563 RC3562A Resistance-Checker, Battery Tester, Milliohm Meter, Software, Manual
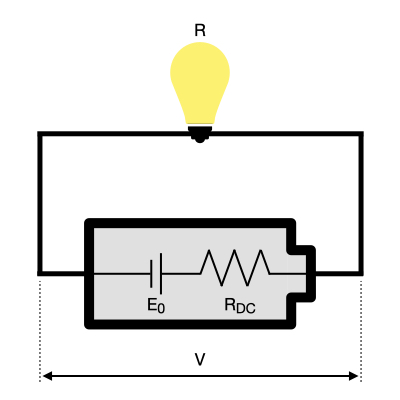
How does the battery internal resistance show in the circuit? The following picture from Hioki learning material shows an example of the internal configuration of a battery. Ideally, a battery’s internal resistance should be zero, allowing for maximum current flow without any energy loss. In reality, however, some internal resistance is always present.
Can the internal resistance be measured to judge whether the battery is good or bad? The answer is usually yes. The same battery will gradually wear out during use, the capacity becomes smaller and smaller, and the internal resistance becomes larger and larger.
When making battery measurements, it is good to know what are the the right internal resistance values to expect.
The typical internal resistance for new high-capacity NiMH rechargeable AA batteries is between 30mΩ and 100mΩ, and for an alkaline battery it is usually between 200mΩ and 300mΩ (but as high as 700mΩ, depending on its charge status). Faulty rechargeable batteries have a much higher internal resistance.
The internal resistance of the new 18650 lithium battery is generally below 50 milliohms, the better is about 20 milliohms, the general is about 30 milliohms. Here is a table for 18650 from https://www.xtar.cc/news/10-things-to-know-about-lithiuim-ion-battery-internal-resistance-224.html with somewhat different numbers:
| Milli-Ohm | Battery Voltage | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| 75-150mOhm | 3.6V | Excellent |
| 150-250mOhm | 3.6V | Good |
| 250-350mOhm | 3.6V | Marginal |
| 350-500mOhm | 3.6V | Poor |
What is the impedance of a 12V battery? The battery internal resistance values varies depending on the battery size. Lead-acid batteries typically have a low impedance, therefore the ability to deliver high currents. Typical impedance for a battery in the standby industry is 12V 80Ah VRLA battery that has typically around 0.003 Ω (3.0mΩ). The short circuit current is typically specified on battery datasheets, e.g., 2,500A for 12V 80 Ah battery. Those values can be used to get idea of the internal resistance (12/2500 = 0.0048 ohms).
A brand new, fully charged 12V lead acid battery typically has an internal resistance around 10-20 milliohms or less. If IR is between 5 to 10 milliohm, it is in good condition. If IR is less than 5 milliohm, it is in very good condition. If IR is between 10 to 30 milliohm, still poor condition but may be usable or revivable. A battery with an internal resistance above 50-60 milliohms is likely nearing the end of its useful life. 12V batteries with IR over 100 milliohms, are likely sulfated, damaged, or otherwise in poor condition and should be replaced.
Typical impedance for a battery in the standby industry:
12V 80Ah VRLA battery = 0.003 Ω (3.0mΩ)
2V 800Ah VRLA battery = 0.0002 Ω (0.2mΩ)
Table with more values from https://xtester.cn/product/RC3563_battery_Internal_resistance_tester.html
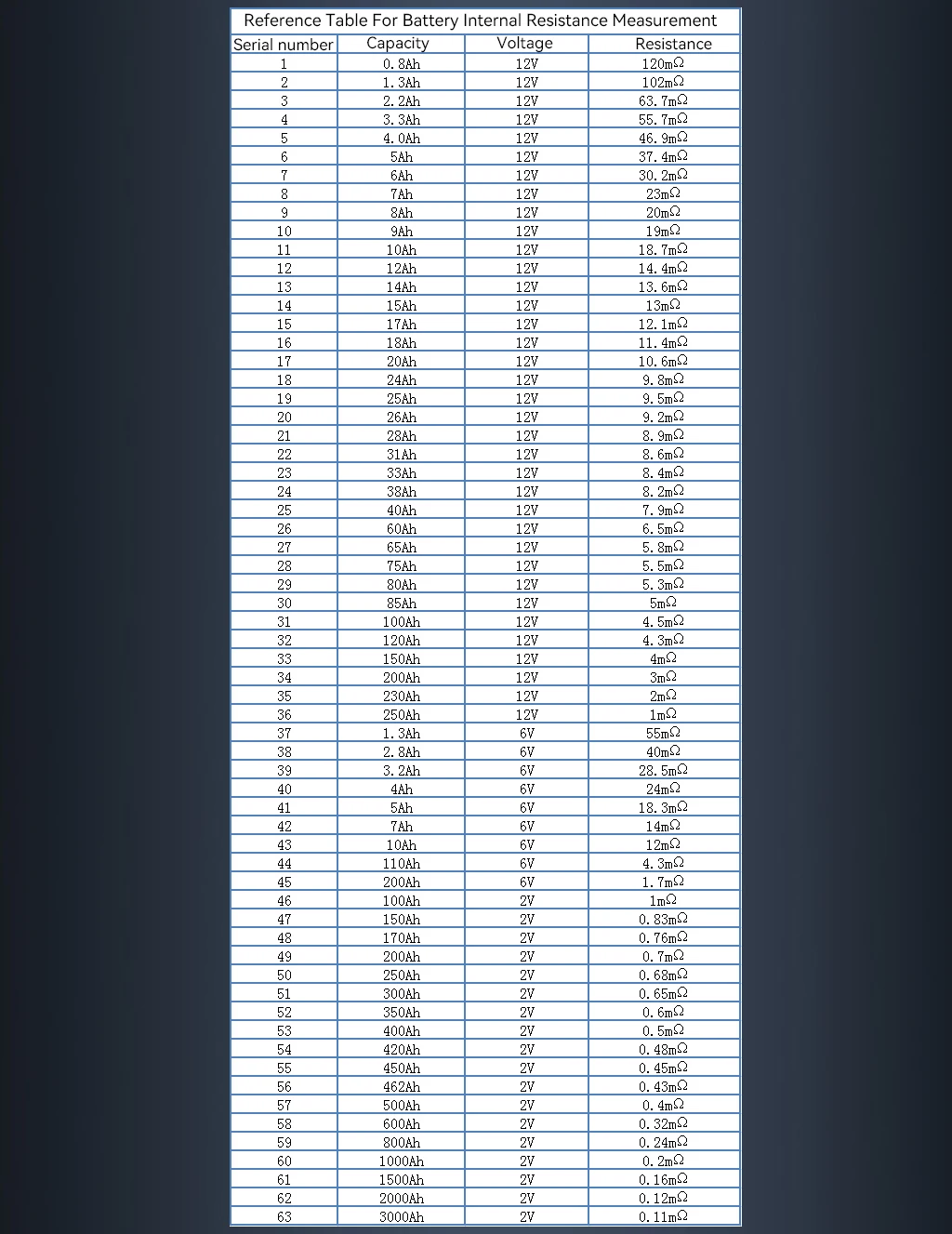
When measuring large-capacity batteries (the internal resistance is very small), you must pay attention to the position of the clip during the measurement. The internal resistance of the battery electrode or connecting wire is often greater than the internal resistance of the battery itself. Pay attention to the position of the clip and make good contact. To get an idea of the size of impedance, let’s compare the typical battery impedances to the resistance of the wire in a standard IEC power lead. The wire length equivalents of the impedances mentioned are 330mm (13.0 inches) and 22mm (0.87inches).
Product links:
https://xtester.cn/product/RC3563_battery_Internal_resistance_tester.html
https://www.amazon.com/LeTkingok-Precision-Handheld-Internal-Resistance/dp/B09HBYBWT8
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/32975204607.html
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005005930826266.html
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005005574356839.html
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005005538739198.html
https://www.aliexpress.com/item/1005005461280358.html
https://hklrf.com/RC3563-Battery-Internal-Resistance-Tester-100V-3Digit-Lead-Acid-Lithium-Battery-Tester-True-4Wire-Auto-Battery-Detector_1885.html
The tester has an USB interface to computer (looks like USB serial port with default baud rate 115200). Here are links to software to get measurement results to computer:
https://github.com/ludwich66/RC3563
https://secondlifestorage.com/index.php?threads/rc3563-ir-tester.8380/page-2#post-79687
The RC3563 is not the only battery resistance tester in the market. Another quite similar is YR1035+/YR1030+ Lithium Battery Internal Resistance Test Instrument that was reviewed in another site.



2 Comments
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://hackaday.com/2024/10/17/the-fnirsi-hrm-10-internal-resistance-meter/
daily pay says:
I’m blown away by the quality and depth of this information. This is the kind of post I’ll be saving and sharing. Amazing work!