Wireless charging for toothbrushes offers a convenient and cable-free solution. Wireless charging eliminates the need for physical connectors or USB cables. Toothbrushes are commonly used in wet environments (bathrooms), and wireless charging systems for toothbrushes can be designed to be water-resistant. It’s a well-known fact that electronics and water do not go together. Most electric brushes fall into the water-resistant category. For the charger itself, the water protection can vary (Oral B chargers I have used seem to be very water resistant).
Most wireless charging toothbrushes use inductive charging technology. This involves the transfer of energy between a charging base (usually a charging dock) and the toothbrush through electromagnetic fields. The charging base is connected to a power source, and the toothbrush contains a coil that receives the energy and converts it into power. Some electric chargers are designed to be used with the matching toothbrush, whereas others are interchangeable. Using a wring type charger can be potentially dangerous and the risks include the charger exploding or catching fire, so be extremely careful.
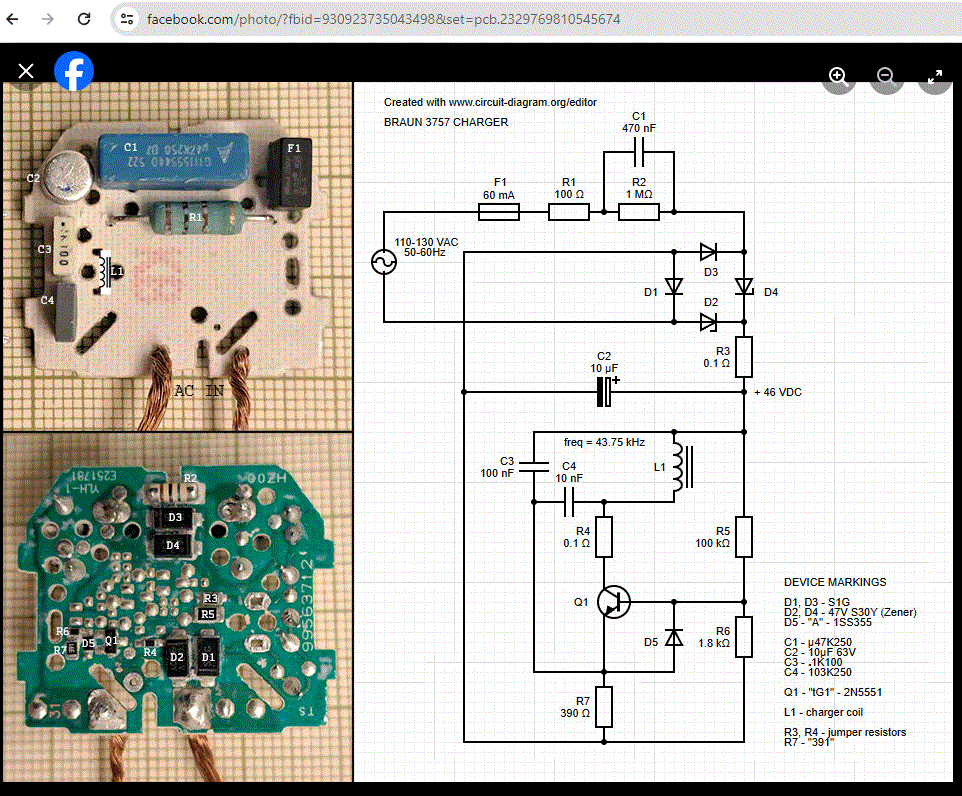
Typically there is a more or less fixed drive to a TX coil, then a RX coil with a rectifier. The power is typically transmitted at high frequency that is typically tens of kHz for efficiency. My own research tells that Oral B chargers seems to operate at around 40 kHz frequency and some other toothbrush work at 80kHz). The primary coil is located in the base of the charger and has an iron (pr other suitable magnetic material) peg on top that’s covered with plastic. When the toothbrush is resting on the peg, you’ll have a complete transformer that works with a magnetic field. Energy goes from the base coil to the secondary coil in the handle through the iron peg.
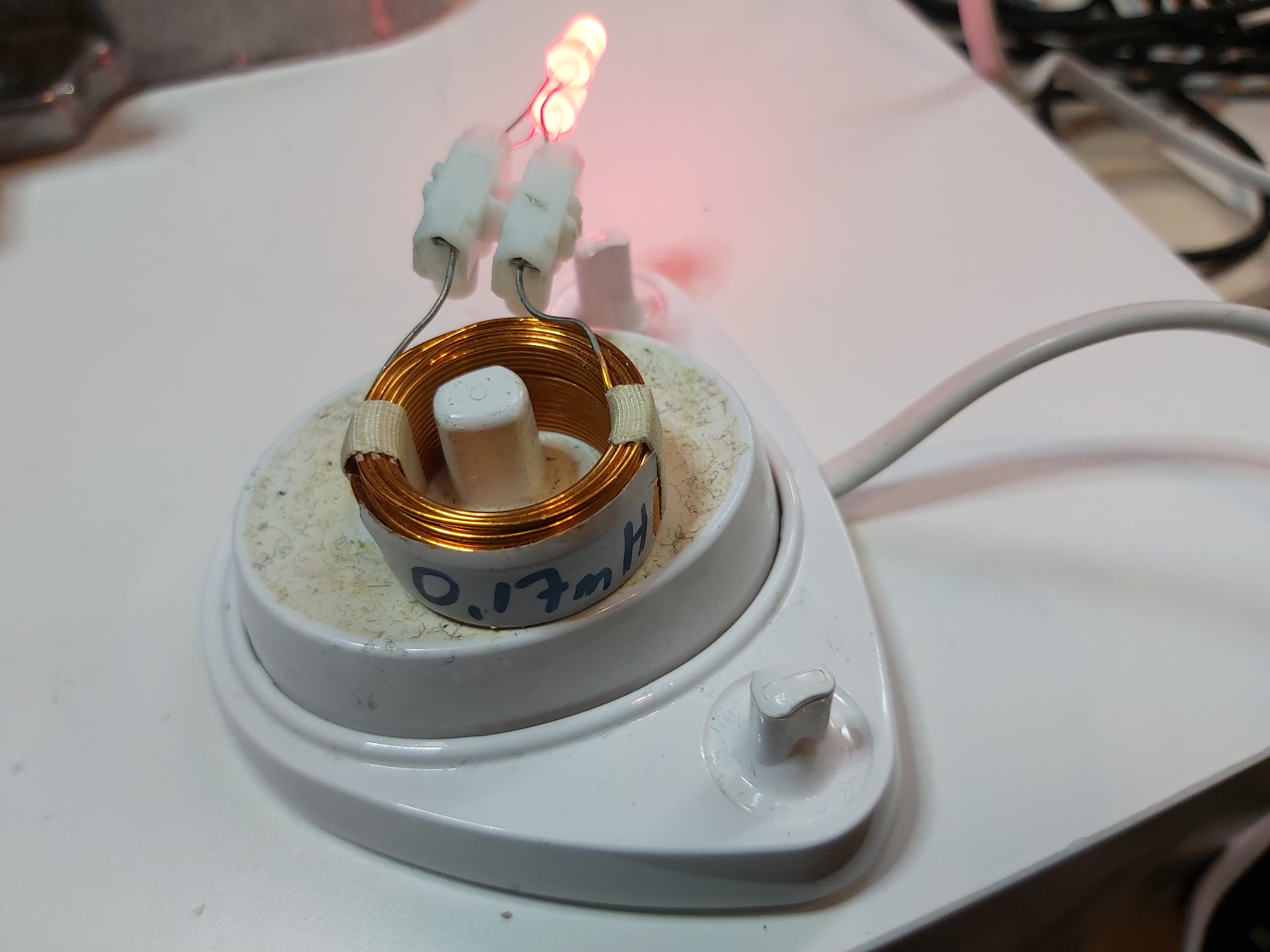
Here is one experiment to power two LEDs using Oral B toothbrush charger. The two LEDs are wired to opposite directions in parallel to the output wires of 0.17 mH coil.
Here is a video on wireless toothbrush charging technology:
Braun Oral-B Electric Toothbrush Teardown (Oscilloscope Action, All the Chips)
More videos on the toothbrush wireless chargers:
Oral-B Precision Electric Toothbrush Battery Replacement | Braun Professional Care Smart Series
Replacing the battery in my Oral-B electric toothbrush
How to replace batteries for an ORAL B Electric toothbrush?
How Does An Electric Toothbrush Charge Itself?
Oral B Toothbrush Charging Induction Voltage
HOW TO CONVERT ORAL-B/BRAUN TOOTHBRUSH CHARGER TO WALL-MOUNT
Braun charger Disassembly video shows that the charger is no easy to disassemble because it potted (to be waterproof).
How to charge your electric toothbrush using a wireless charger!!
Some technical description of the wireless charging system:
Why Your Braun Oral-B or Sonicare Toothbrush Is Not Charging document tells that a charging problem is quite common and can sometimes be mis-diagnosed as a faulty charger/faulty battery when the opposite is true.
Someone dissolved the plastic of the Oral B charging device
https://m.facebook.com/groups/ElectronicParts/permalink/2329769810545674/
This circuit looks quite simple.
There is discussion on charger circuit at https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/454305/wireless-power-transfer-for-a-toothbrush
Wireless Charging Vibration Electric Toothbrushes technical note from Holtek at
https://www.holtek.com/webapi/5905185/WAS-20A1EN_ReferenceDesign.pdf says:
Wireless charging vibration electric toothbrushes are divided into two parts, a wireless charging
transmitter or charging base and a vibration electric toothbrush or toothbrush body. The charging
base mainly includes two functions, wireless charging and ID identification. The toothbrush body
includes four functions, wireless charging, lithium battery charging/discharging management,
vibration motor control and LED indicators. The charging base is powered by a 5V USB interface
and provides power to the toothbrush body through LC resonance, which provides a one-way
communication function, so that the charging base can receive information and identify ID
information returned by the toothbrush body. The toothbrush body provides charging over voltage
protection and LED battery level display functions during the charging process.
The Holtek dedicated wireless charging MCU provides the required control signals mentioned
above
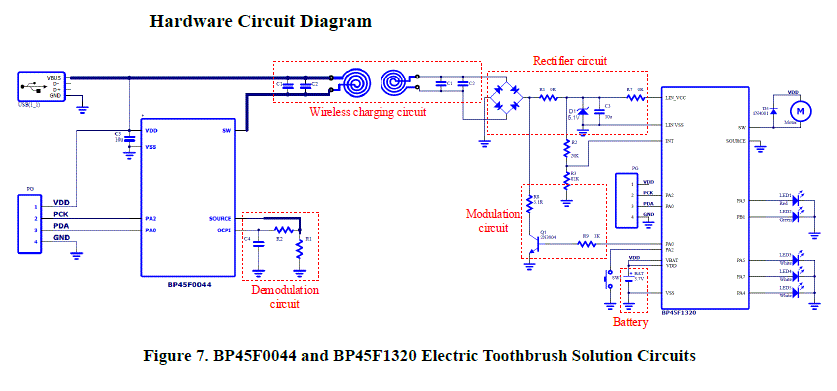
The page 7 of the Wireless Charging Vibration Electric Toothbrushes document has a schematics of an USB powered charging circuit.
This reference design is composed of a charging base and a toothbrush body. The charging base uses the BP45F0044 as a master MCU and provides 0.5K of Flash Program Memory, 4 bidirectional I/Os, a high voltage NMOS, a programmable PWM circuit and a demodulation circuit.
After receiving the LC resonance energy signal transmitted by the charging base, the toothbrush body will pass through a full-bridge rectifier circuit and a Zener regulator circuit, then provide power to the BP45F1320 linear charging circuit. The communication method for this reference design is based on load changes – changing load current.



2 Comments
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.66pacific.com/calculators/coil-inductance-calculator.aspx
Tomi Engdahl says:
https://www.learningaboutelectronics.com/Articles/Inductor-impedance-calculator.php#answer